How to Ensure Email Deliverabilty & Comply with Sender Requirements
Email deliverability is critical for the success of your email marketing campaigns. This document outlines a few steps you can take to ensure your emails reach your recipients’ inboxes reliably.
This article outlines the steps necessary to comply with the new Google & Yahoo email sender requirements going into effect in February 2024.
Step 1. Authenticate your domains
By default, we deliver emails using a shared @userlistmail.com domain. This domain is fully managed and authenticated by Userlist. However, that also means that your own domain is not included in the email’s From header, but only the Reply-To header.
We strongly recommend using your own custom sending domain to improve deliverability and ensure that all replies reach your inbox.
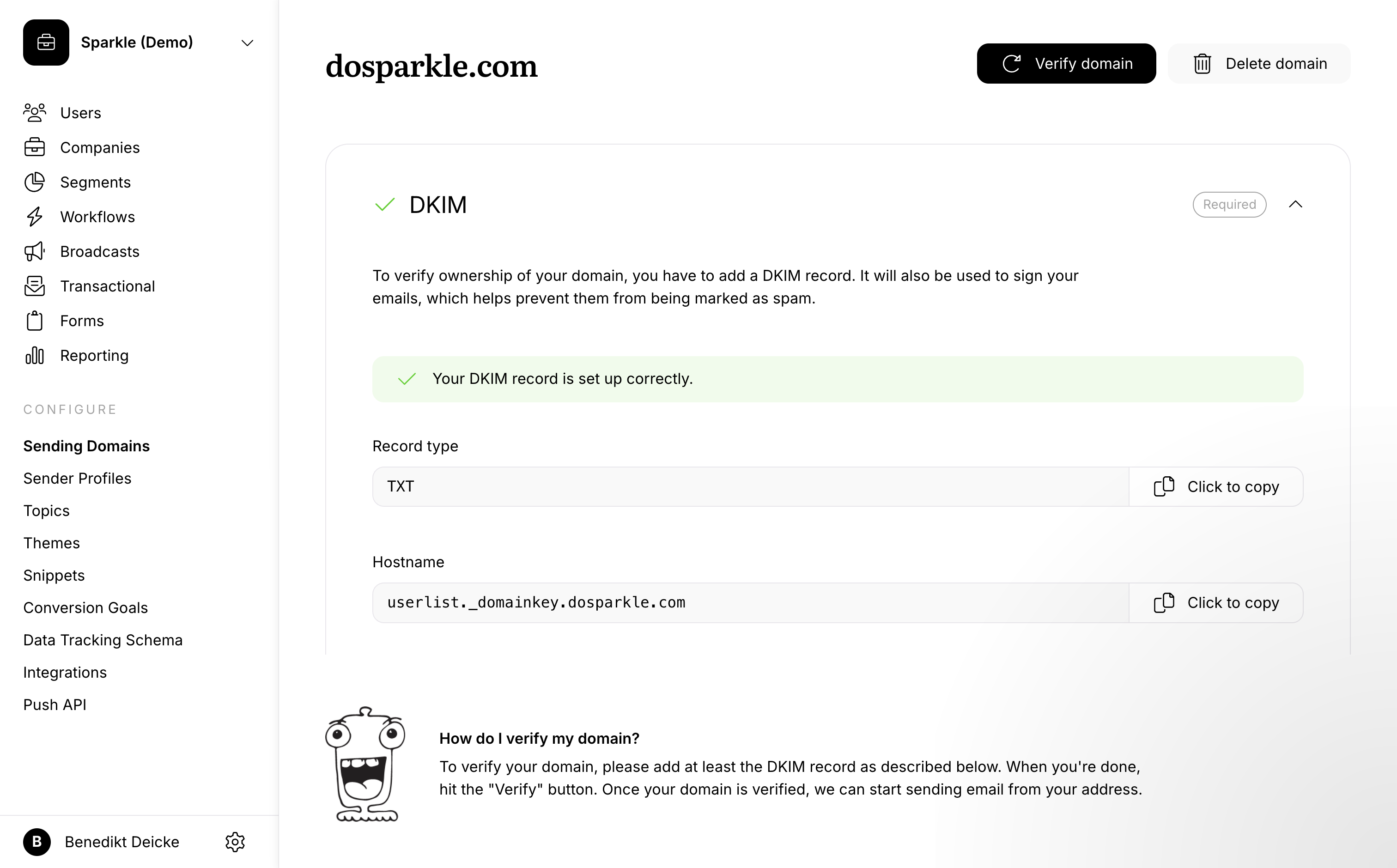
DKIM authentication
When setting up a new custom domain with Userlist, we ask you to set up a DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) DNS record on your domain. This allows us to verify that you’re the owner of the domain, but also lets the receiving mail server know that messages we send are legitimate emails from your domain.
SPF authentication
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) authentication is another important factor to ensure that your emails are delivered to your recipients’ inboxes. SPF is a method used to prevent sender address forgery, increasing your email’s legitimacy and improving overall deliverability.
As an email service provider, we handle SPF authentication for you. This is achieved by sending your emails including our own bounce domain, which is already properly SPF authenticated.
If you’d like to use a custom bounce domain to achieve SPF aligment, please reach out to us via our support address.
DMARC policy
Implementing a DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting & Conformance) policy is essential for ensuring deliverability with major providers such as Google and Yahoo. DMARC helps in verifying that the sender’s email messages are protected by SPF and/or DKIM, and it informs email providers how to handle non-compliant emails. Setting up a DMARC policy involves adding a specific DNS record to your domain.
-
Start by adding a DMARC record with a policy of ‘none’ to your domain. This setting doesn’t affect your email delivery but allows you to gather reports on your email sources and identify issues. The record looks like
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:your_email@example.com, whereruais the address for sending aggregate reports. While you can use your own email address for this, we recommend using a dedicated monitoring tool like Postmark’s free DMARC monitoring tool. -
You’ll start receiving reports about all email activity for your domain. Monitor these closely to identify which email servers and tools are sending emails on your domain’s behalf. Make sure that all legitimate senders are properly passing DKIM and SPF checks.
-
After reviewing reports and ensuring most outbound emails comply with SPF and DKIM, change the DMARC policy from ‘none’ to ‘quarantine’. You can start with a small percentage of emails, e.g.,
v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; pct=10. This will instruct receiving mail servers to put 10% of the emails that are not properly authenticated into the recipient’s spam folder. -
Keep monitoring the reports to check how quarantined emails are being handled. Gradually increase the percentage (
pct) of emails under the quarantine policy as you gain confidence in your SPF and DKIM compliance. -
Once your legitimate email servers are compliant and you’ve tested with the quarantine policy, switch to a ‘reject’ policy for increased security. This instructs receiving mail servers to not accept unauthenticated emails at all.
After you’ve set up your DMARC policy, keep monitoring the DMARC reports on a regular basis to notice possible issues early.
Step 2. Provide support for one-click unsubscribes
Major providers like Google and Yahoo require all commercial and marketing emails to have support for one-click according to RFC 8058. This allows recipients to unsubscribe from all emails with a single click within their email client.
In Userlist, all emails that are not explicitly marked as transactional include an unsubscribe link in the footer as well as the required headers to comply with RFC 8058. This works out of the box, and no action is required.
Step 3. Keep your spam rates low
As you start sending your workflows and broadcasts, make sure your customers are expecting your emails and not marking them as spam.
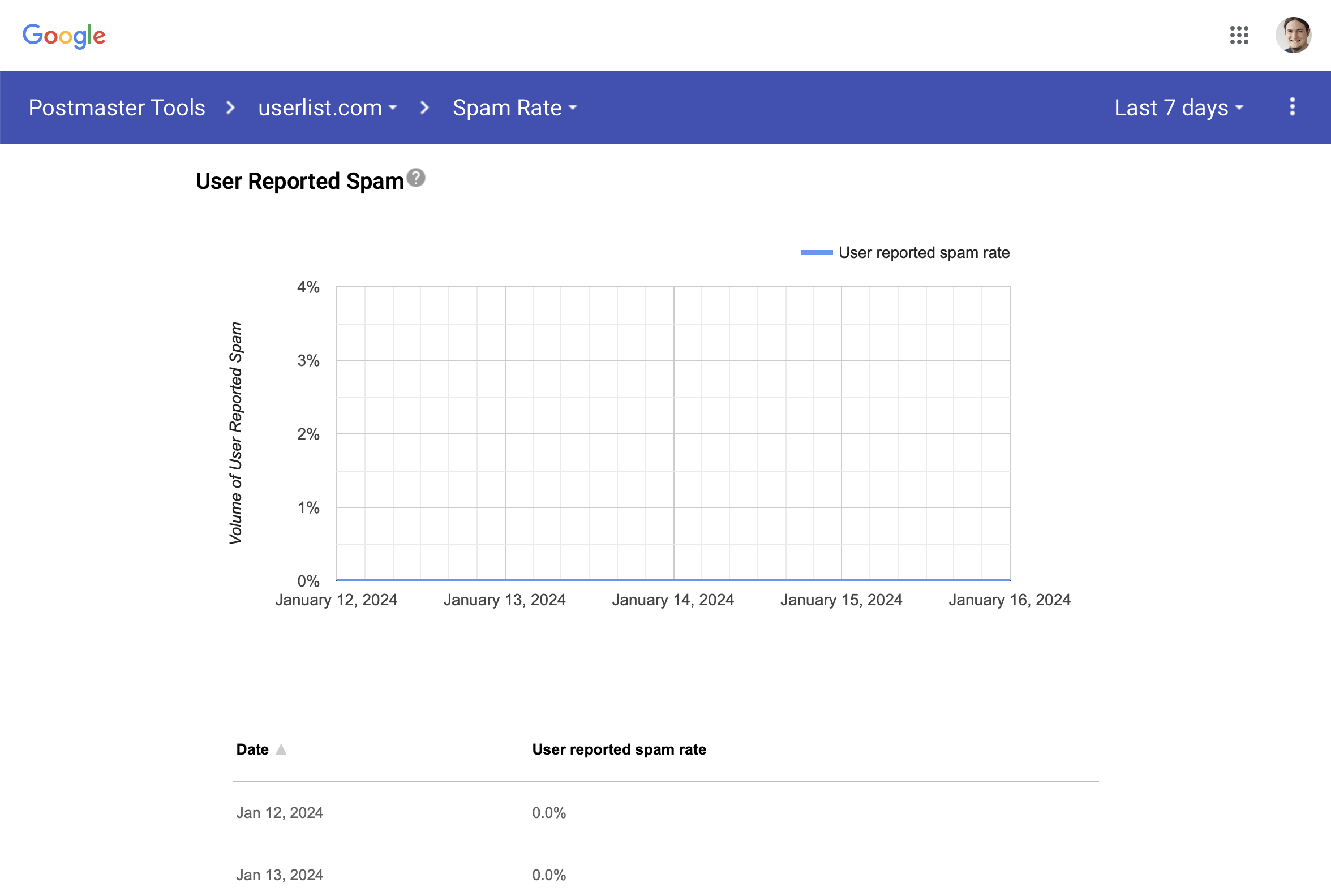
Google requires all senders of bulk emails to keep their spam complaint rates below 0.10% without exceeding a threshold of 0.30%. You can monitor your spam rate with Google using the Google Postmaster Tools.
Need assistance?
If you have additional questions or need assistance to comply with any of the requirements mentioned above, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.